butt weld fittings are defined as a part used in a piping system, for changing direction, branching or for change of pipe diameter, and which is mechanically joined to the system.
There are many different types of fittings and they are the same in all sizes and schedules as the pipe.
Fittings are pided into three groups:
1.Buttweld (BW) fittings whose dimensions, dimensional tolerances et cetera are defined in the ASME B16.9 standards. Light-weight corrosion resistant fittings are made to MSS SP43.
2.Socket Weld (SW) fittings Class 3000, 6000, 9000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
3.Threaded (THD) fittings Class 2000, 3000, 6000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
• APPLICATIONS OF BUTTWELD FITTINGS
A piping system using buttweld fittings has many inherent advantages over other forms.
1. Welding a fitting to the pipe means it is permanently leakproof
2. The continuous metal structure formed between pipe and fitting adds strength to the system
3. Smooth inner surface and gradual directional changes reduce pressure losses and turbulence and minimize the action of corrosion and erosion
4. A welded system utilizes a minimum of space
• BEVELLED ENDS
The ends of all buttweld fittings are bevelled, exceeding wall thickness 4 mm for austenitic stainless steel, or 5 mm for ferritic stainless steel. The shape of the bevel depending upon the actual wall thickness. This bevelled ends are needed to be able to make a “Butt weld”.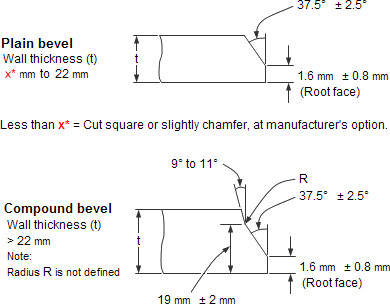
ASME B16.25 covers the preparation of buttwelding ends of piping components to be joined into a piping system by welding. It includes requirements for welding bevels, for external and internal shaping of heavy-wall components, and for preparation of internal ends (including dimensions and dimensional tolerances). These weld edge preparation requirements are also incorporated into the ASME standards (e.g., B16.9, B16.5, B16.34).
• MATERIAL AND PERFORMANCE
The most common materials used in fittings produced is carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, aluminium, copper, the various types of plastics, et cetera et cetera.
In addition, fittings, like pipes, for specific purposes sometimes internally equipped with layers of materials of a completely different quality as the fitting themselves, which are “lined fittings”.
The material of a fitting is basically set during the choice of the pipe, in most cases, a fitting is of the same material as the pipe.






0 comments:
Post a Comment